Seed Dissection Activity The Sylvia Center
Definition of Seed: A true seed is defined as a fertilized mature ovule that possesses embryonic plant, stored material, and a protective coat or coats. Seed is the reproductive structure characteristic of all phanerogams. The structure of seeds may be studied in such common types of pea, gram, bean almond or sunflower.
.PNG)
Reproduction in Flowering Plants Presentation Biology
by Ben Bareja Last Updated April 10, 2022 There are three basic parts of a seed in the angiosperms: (a) an embryo, (b) food storage or nutritive tissue, and (c) seed covering. Embryo A mature seed has a diploid (2N) embryo which develops from a fertilized egg or zygote.
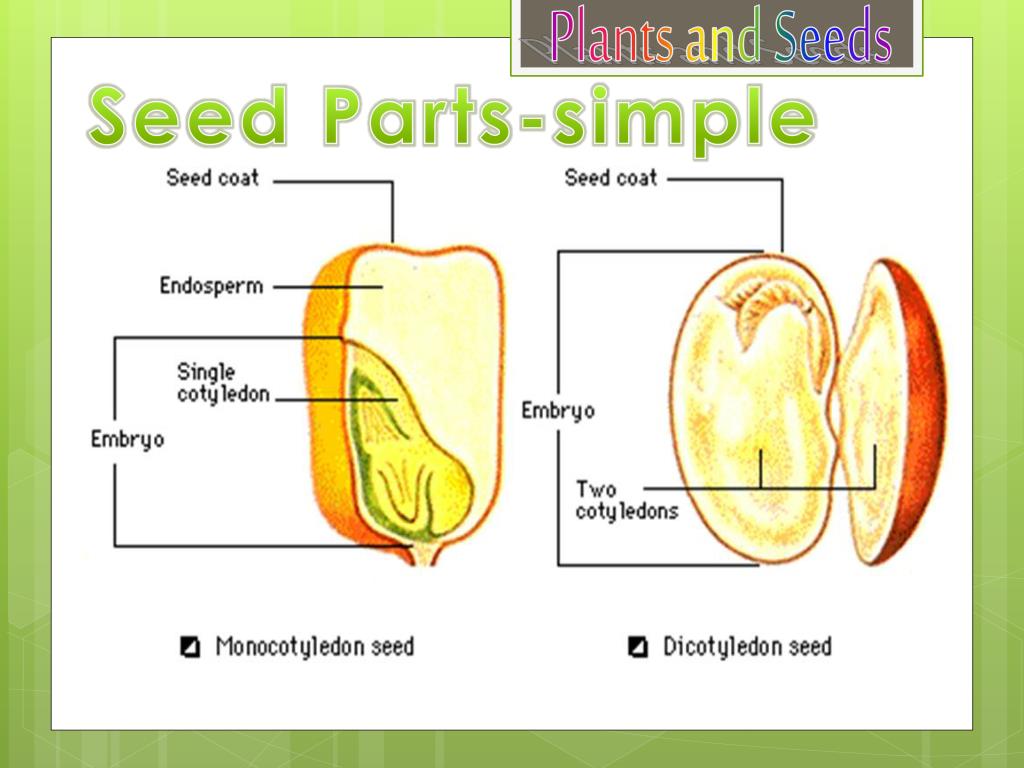
PPT Plants and Seeds PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID791432
Seeds and diversity. To review, the two fundamental ways of propagating plants and how they differ in their outcomes are s exual reproduction through seeds or spores, and a sexual or vegetative reproduction through manipulation of various plant parts, including cuttings from leaves, roots, and stems, or grafting.. Asexual reproduction, also called vegetative propagation, normally results in.

BBE 1st Grade Science Lab! Gardening & Plant parts
This article provides a diagram of the various parts of a seed, including the seed coat, embryo, endosperm, and cotyledons. Learn about the function and structure of each part and how they contribute to the growth and development of a plant from a seed. Skip to content Circuitry Blueprint Depot Browse Our Electronic Schematic Designs
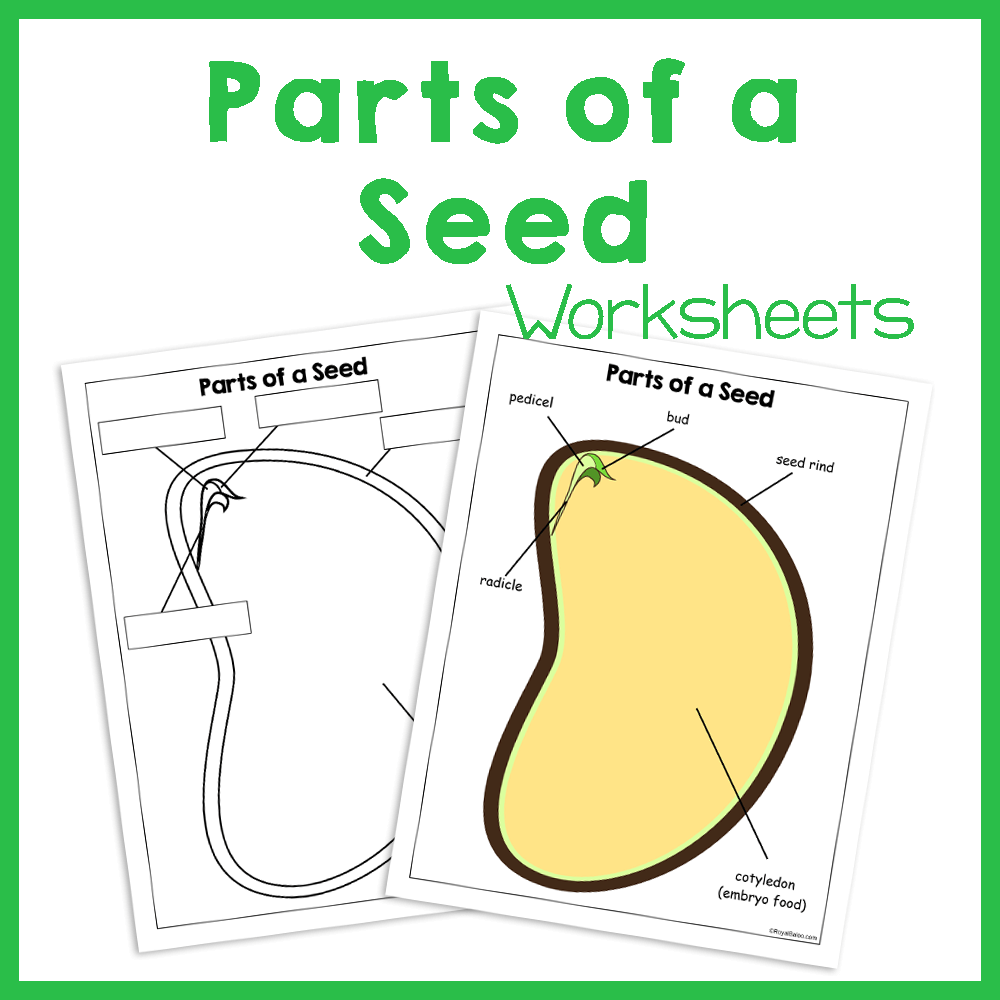
Parts Of A Seed cloudshareinfo
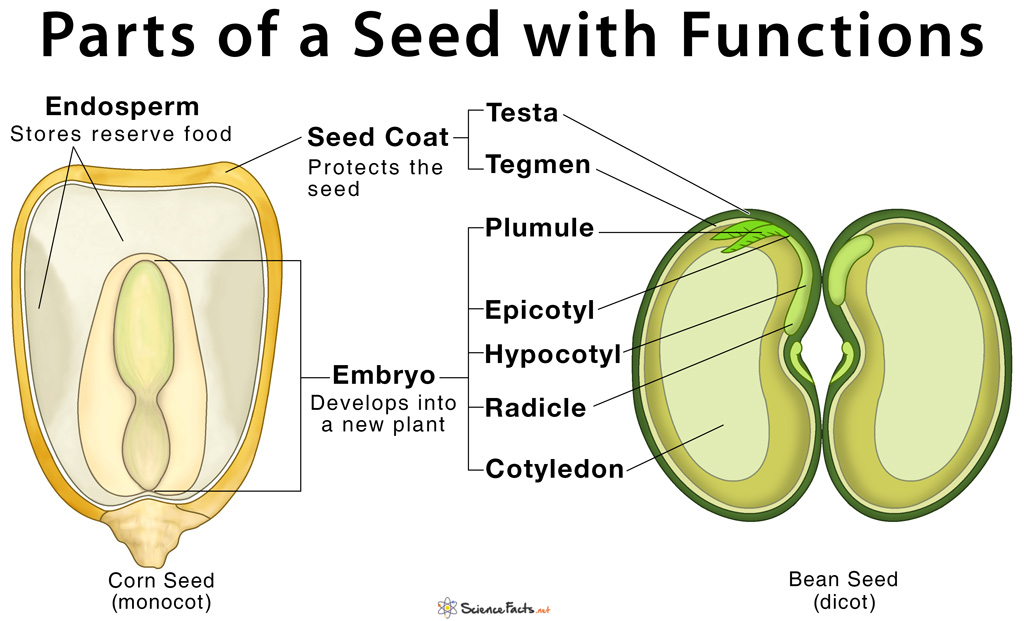
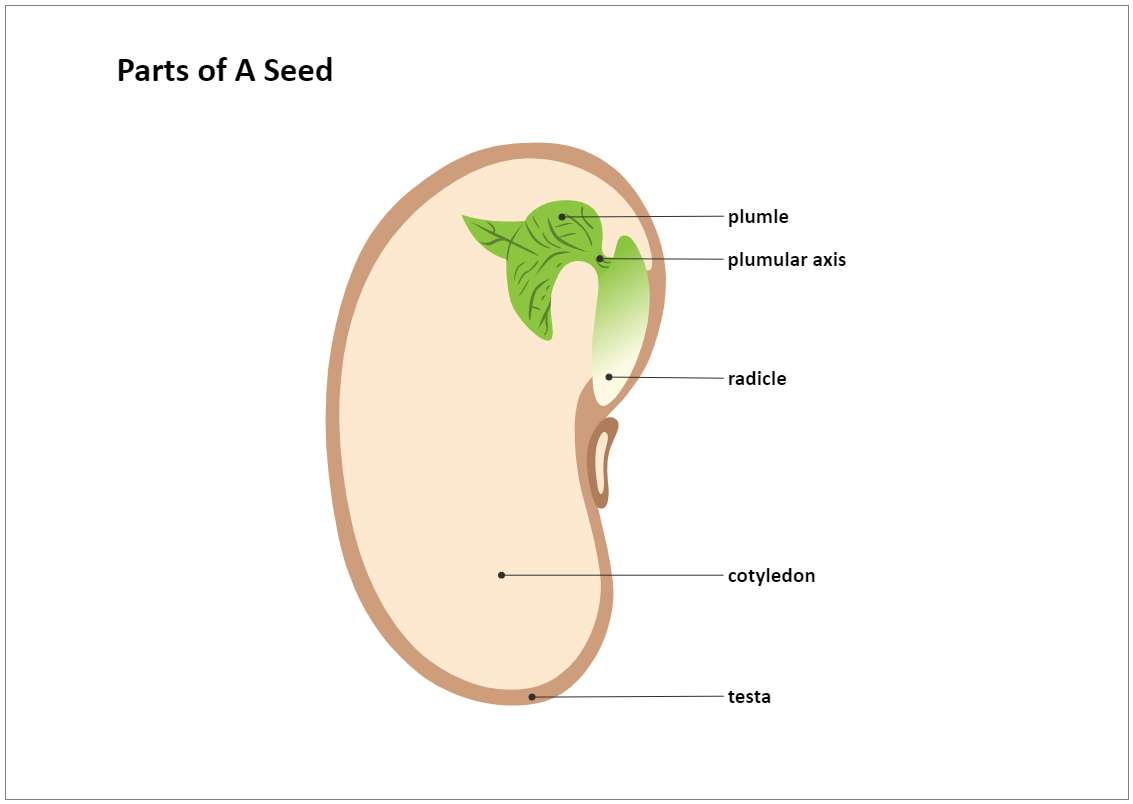
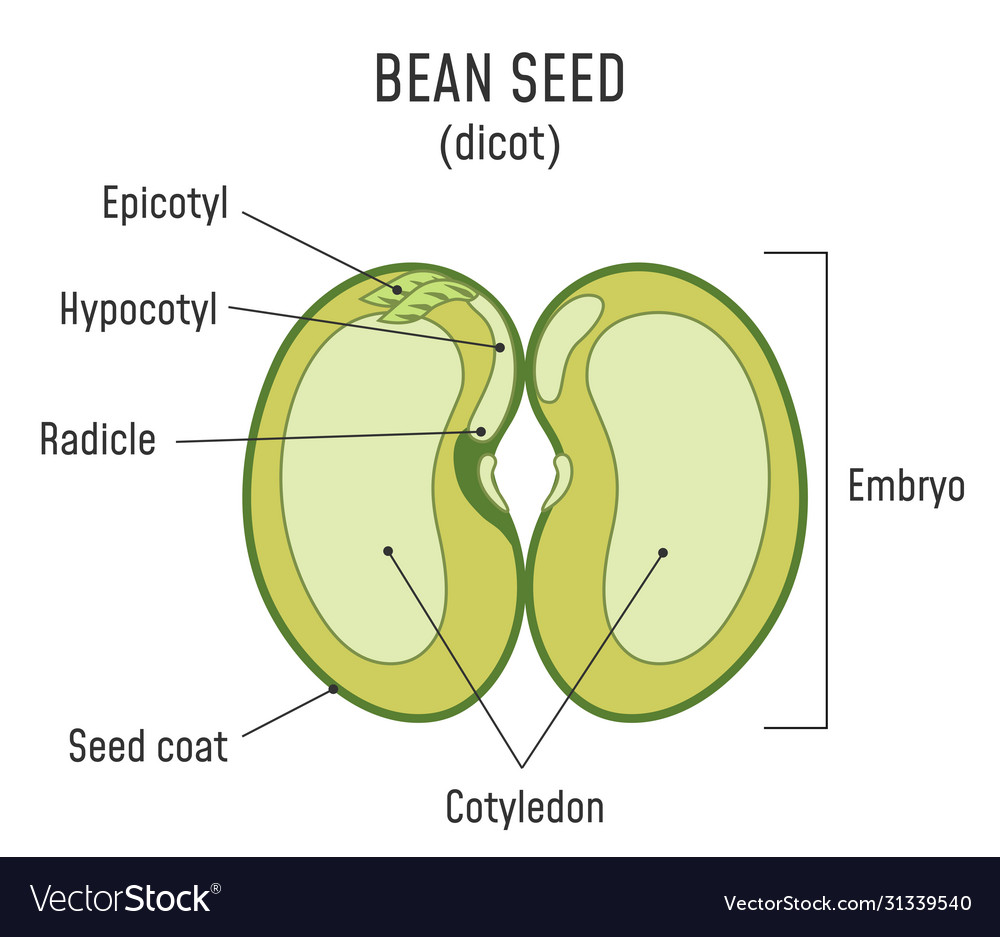
It consists of three parts: a plumule that forms the shoot, a hypocotyl that forms the stem, and a radicle that forms the root. Structures of dicot and monocot seeds - LibreTexts (CC BY-NC-SA) The seed coat consists of one (in monocots) or more (in dicots) protective layers that encase the seed. In dicots, the seed coat is divided into an.
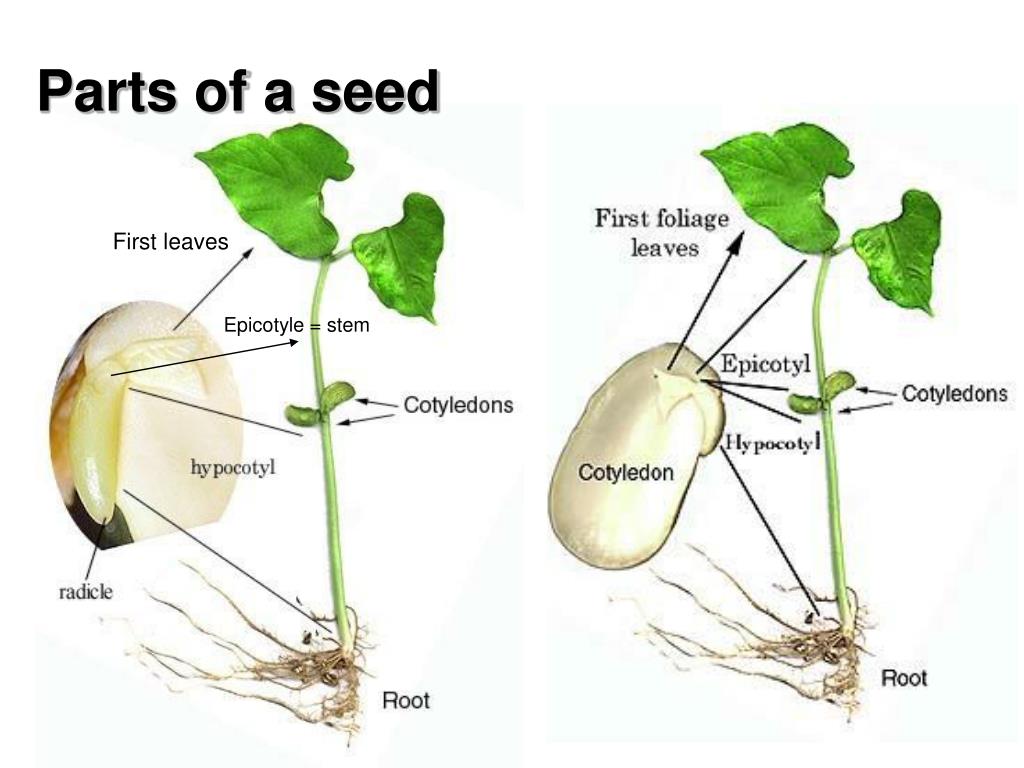
PPT Seeds and Growing Plants PowerPoint Presentation ID229013
The seed has several parts such as epicotyl, hyp. #seed #howtodraw #biologyThis is a diagram of the seed. You can learn to draw and color the parts of a seed.

What Are the Parts of a Seed? Science NetLinks Afterschool
Seed Anatomy. Here you can see, I've removed the seed coat and split the seed in half. One half has the embryo and some of the stored food, and the other half holds the rest of the stored food. This picture is of the half of the seed that has the embryo. This picture is a close-up of the embryo. You can see the part of the embryo called the.

1. Draw a diagram of seed and label its parts. Mention the functions of
A mature seed has an embryo with a linear arrangement of parts. This arrangement is called the embryo axis. The drawing above shows the embryo axis from the kidney bean, straightened out to show the individual structures. Embryo axis — the embryonic root and shoot; Parts making up the shoot tissue of the embryo axis:

Seed Plant Seed Definition, Parts, Types, Structure, Functions
Seed Growth. In angiosperms, the process of seed development begins with double fertilization and involves the fusion of the egg and sperm nuclei into a zygote. The second part of this process is the fusion of the polar nuclei with a second sperm cell nucleus, thus forming a primary endosperm. Right after fertilization, the zygote is mostly.
Plants are clever. 2 Wildlife and Ecology, the Wildlife Encyclopaedia
The parts of a bean seed (a dicot), showing the seed coat and embryo Diagram of the internal structure of a dicot seed and embryo: (a) seed coat, (b) endosperm, (c) cotyledon, (d) hypocotyl. A typical seed includes two basic parts: an embryo; a seed coat.

Parts Of A Seed cloudshareinfo
Learn about the parts of a seed and draw your own diagram.

Label the Parts of a Seed Animal Jam Academy
A typical seed consists of the following parts: Source: Google Tesla: It is the outer coat of the seed that protects the embryonic plant. Micropyle: It is a tiny pore in the testa that lies on the opposite of the tip of the radicle. It permits water to enter the embryo before active germination.

Anatomy Of A Bean Seed Stock Vector Art & More Images of Agriculture
seed, the characteristic reproductive body of both angiosperms (flowering plants) and gymnosperms (e.g., conifers, cycads, and ginkgos).Essentially, a seed consists of a miniature undeveloped plant (the embryo), which, alone or in the company of stored food for its early development after germination, is surrounded by a protective coat (the testa).). Frequently small in size and making.
Parts of A Seed Diagram EdrawMax Template
A seed has three parts: Seed Coat Endosperm Embryo Seed Coat A seed coat protects the internal parts of a seed. The seed coat has two layers. The outer layer is thick and known as the testa. The inner layer is thin and known as tegmen. A thick seed coat protects the seed from sunlight and water.

Parts Of A Seed Printable Printable Word Searches
A seed consists of the following parts: Hilum - It is a scar that is located on the seed coat, associated with the stalk of the plant. Seed coat - Forms the exterior covering of the plant, supplying with nourishment and protection to the seed inside. Endosperm - It is the tissue containing nutrients for the growth of the embryo.
Bean seed structure anatomy grain dicot seed Vector Image
Instructor: Emily Lockhart Emily has taught science and has a master's degree in education. Cite this lesson Explore the parts of a seed and discover interesting facts about how it becomes a.